The concept of the network edge has gained prominence with the rise of edge computing, which involves processing data closer to the source of data generation rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. This approach can reduce latency, improve efficiency, and enhance the overall performance of applications and services. In this article, we’ll introduce what the network edge is, explore how it differs from edge computing, and describe the benefits that network edge brings to enterprise data environments.
What is Network Edge?
At its essence, the network edge represents the outer periphery of a network. It’s the gateway where end-user devices, local networks, and peripheral devices connect to the broader infrastructure, such as the internet. It’s the point at which a user or device accesses the network or the point where data leaves the network to reach its destination. the network edge is the boundary between a local network and the broader network infrastructure, and it plays a crucial role in data transmission and connectivity, especially in the context of emerging technologies like edge computing.
What is Edge Computing and How Does It Differ from Network Edge?
The terms “network edge” and “edge computing” are related concepts, but they refer to different aspects of the technology landscape.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that involves processing data near the source of data generation rather than relying on a centralized cloud-based system. In traditional computing architectures, data is typically sent to a centralized data center or cloud for processing and analysis. However, with edge computing, the processing is performed closer to the “edge” of the network, where the data is generated. Edge computing complements traditional cloud computing by extending computational capabilities to the edge of the network, offering a more distributed and responsive infrastructure.
” Also Check – What Is Edge Computing?
What is the Difference Between Edge Computing and Network Edge?
While the network edge and edge computing share a proximity in their focus on the periphery of the network, they address distinct aspects of the technological landscape. The network edge is primarily concerned with connectivity and access, and it doesn’t specifically imply data processing or computation. Edge computing often leverages the network edge to achieve distributed computing, low-latency processing and efficient utilization of resources for tasks such as data analysis, decision-making, and real-time response.
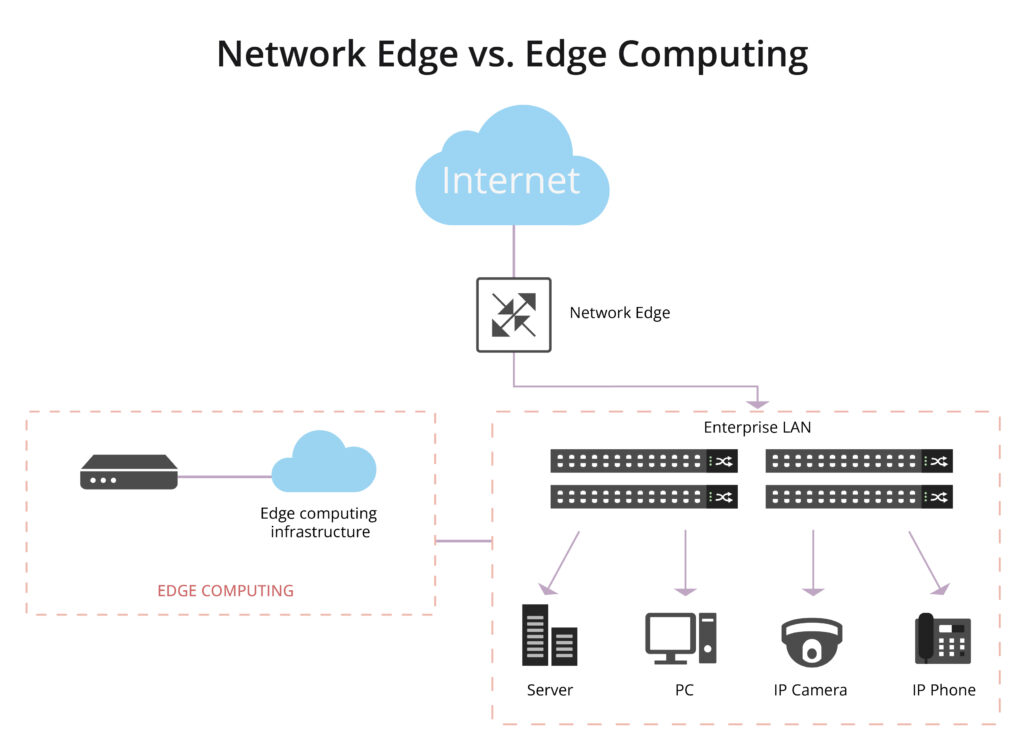
Network Edge vs. Network Core: What’s the Difference?
Another common source of confusion is discerning the difference between the network edge and the network core.
What is Network Core?
The network core, also known as the backbone network, is the central part of a telecommunications network that provides the primary pathway for data traffic. It serves as the main infrastructure for transmitting data between different network segments, such as from one city to another or between major data centers. The network core is responsible for long-distance, high-capacity data transport, ensuring that information can flow efficiently across the entire network.
What is the Difference between the Network Edge and the Network Core?
The network edge is where end-users and local networks connect to the broader infrastructure, and edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, the network core is the backbone that facilitates the long-distance transmission of data between different edges, locations, or network segments. It is a critical component in the architecture of large-scale telecommunications and internet systems.
Advantages of Network Edge in Enterprise Data Environments
Let’s turn our attention to the practical implications of edge networking in enterprise data environments.
Efficient IoT Deployments
In the realm of the Internet of Things (IoT), where devices generate copious amounts of data, edge networking shines. It optimizes the processing of IoT data locally, reducing the load on central servers and improving overall efficiency.
Improved Application Performance
Edge networking enhances the performance of applications by processing data closer to the point of use. This results in faster application response times, contributing to improved user satisfaction and productivity.
Enhanced Reliability
Edge networks are designed for resilience. Even if connectivity to the central cloud is lost, local processing and communication at the edge can continue to operate independently, ensuring continuous availability of critical services.
Reduced Network Costs
Local processing in edge networks diminishes the need for transmitting large volumes of data over the network. This not only optimizes bandwidth usage but also contributes to cost savings in network infrastructure.
Privacy and Security
Some sensitive data can be processed locally at the edge, addressing privacy and security concerns by minimizing the transmission of sensitive information over the network. Improved data privacy and security compliance, especially in industries with stringent regulations.
In this era of digital transformation, the network edge stands as a gateway to a more connected, efficient, and responsive future.
Related Articles:
