Since the customers have demanded for a more intensive bandwidth, the telecommunication carriers must seek to offer a matured network convergence and enable the revolution of consumer media device interaction. Hence, the emergence of FTTx technology is significant for people all over the world. FTTx, also called as fiber to the x, is a collective term for any broadband network architecture using optical fiber to provide all or part of the local loop used for last mile telecommunications. With different network destinations, FTTx can be categorized into several terminologies, such as FTTH, FTTN, FTTC, FTTB, FTTP, etc. The following parts will introduce the above terms at length.
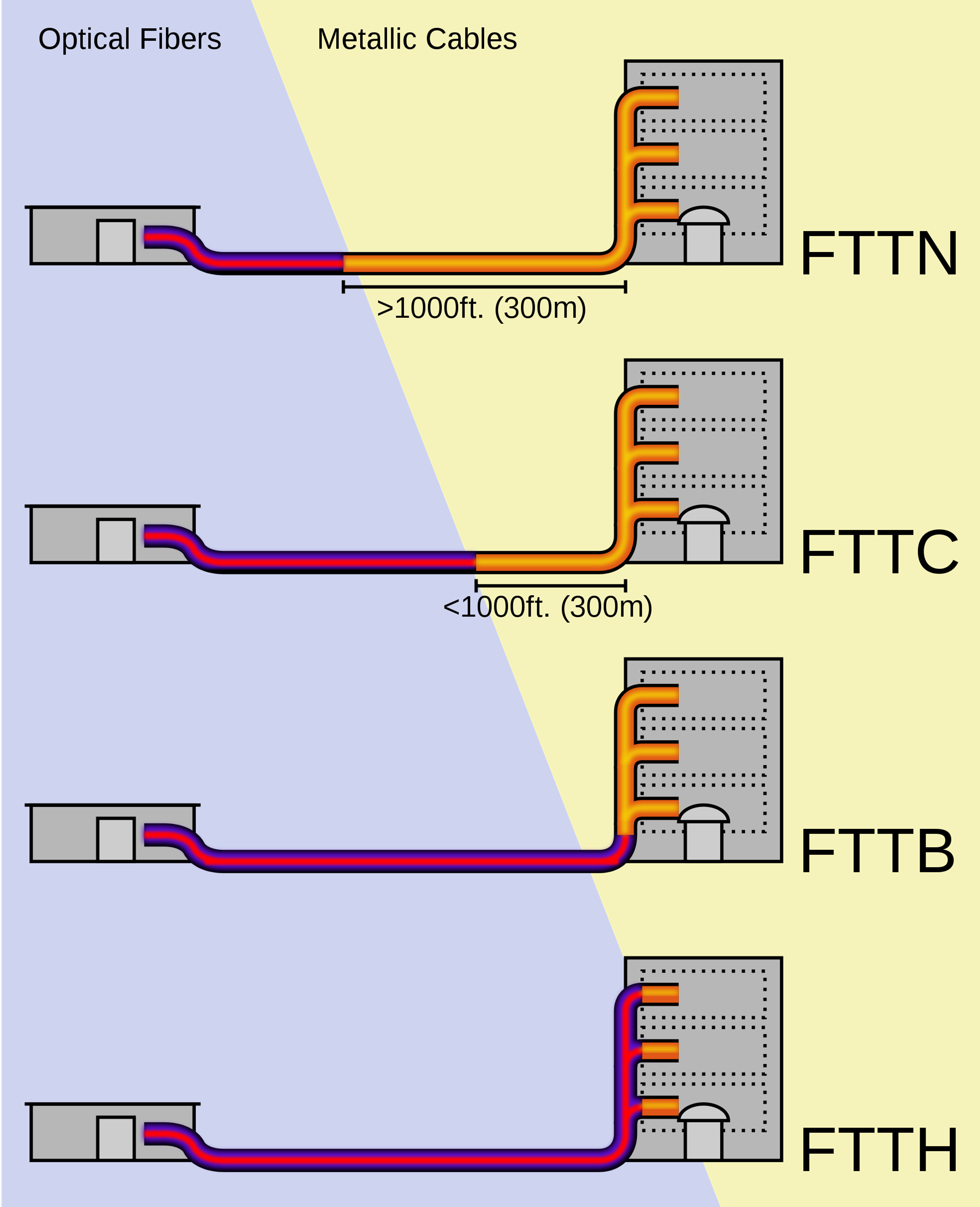
FTTx is commonly associated with residential FTTH (fiber to the home) services, and FTTH is certainly one of the fastest growing applications worldwide. In an FTTH deployment, optical cabling terminates at the boundary of the living space so as to reach the individual home and business office where families and officers can both utilize the network in an easier way.
In a FTTN (fiber to the node) deployment, the optical fiber terminates in a cabinet which may be as much as a few miles from the customer premises. And the final connection from street cabinet to customer premises usually uses copper. FTTN is often an interim step toward full FTTH and is typically used to deliver advanced triple-play telecommunications services.
In a FTTC (fiber to the curb) deployment, optical cabling usually terminates within 300 yards of the customer premises. Fiber cables are installed or utilized along the roadside from the central office to home or office. Using the FTTC technique, the last connection between the curb and home or office can use the coaxial cable. It replaces the old telephone service and enables the different communication services through a single line.
In a FTTB (fiber to the building) deployment, optical cabling terminates at the buildings. Unlike FTTH which runs the fiber inside the subscriber’s apartment unit, FTTB only reaches the apartment building’s electrical room. The signal is conveyed to the final distance using any non-optical means, including twisted pair, coaxial cable, wireless, or power line communication. FTTB applies the dedicated access, thus the client can conveniently enjoy the 24-hour high speed Internet by installing a network card on the computer.
FTTP (fiber to the premise) is a North American term used to include both FTTH and FTTB deployments. Optical fiber is used for an optical distribution network from the central office all the way to the premises occupied by the subscriber. Since the optical fiber cable can provide a higher bandwidth than copper cable over the last kilometer, operators usually use FTTP to provide voice, video and data services.
With its high bandwidth potential, FTTx has been closely coupled with triple play of voice, video and data services. And the world has now evolved beyond triple play to a converged multi-play services environment with a high bandwidth requirement. Applications like IPTV, VOIP, RF video, interactive online gaming, security, Internet web hosting, traditional Internet and even smart grid or smart home are widely used in FTTx network.
FTTx technology plays an important part in providing higher bandwidth for global networks. According to different network architectures, FTTx is divided into FTTH, FTTN, FTTC, FTTB, FTTP, etc. FS.COM provides FTTx solutions and tutorials for your project, please visit FS.COM for more information.
