As the basis of upgrading network, 10G network has been ubiquitous in data center, enterprise network and even home networking. 10GBASE-T and SFP+ transceiver are two different kinds of technology which transmit data via copper and fiber respectively. 10GBASE-T technology provides the most flexible and economical solution while 10G SFP+ offers the compatible and user-friendly solution for 10G Ethernet connectivity option. This article would shed light on 10GBASE-T vs SFP+.
10GBASE-T Technology
As the fourth generation of IEEE standardized Base-T technologies, 10GBASE-T is designed to reduce overall costs and improve flexibility. By using RJ45 connectors and unshielded twisted pair cabling, 10GBASE-T allows 10Mbps, 100Mbps, 1Gbps, and 10Gbps data transmission, while being backward-compatible with prior generations. Merits and demerits of using 10GBASE-T are listed in the below.
- Cheap twisted pair cables.
- Patch panels can be used without messing around with transceivers.
- Higher power consumption.
- People may get tempted to use substandard cabling, and this would have a negative influence on the speed.
- No good way to extend length beyond 100m (though this can be somewhat mitigated by choosing switches with mostly 10GBASE-T but also a handful of SFP+ ports) limited choice of equipment.
10G SFP+ Technology
The 10G SFP+ transceiver meets the standard of Multi-Sourcing Agreement (MSA), and provides the cost effective solution for 10G optical data communication. It supports both duplex and simplex LC optics interfaces. The 10G SFP+ transceiver consists of 10Gbit/s DFB/EML optical transmitter and PIN receiver, which allow 300m~120km 10G Ethernet and 10G fiber channel applications. Advantages and disadvantages of using 10G SFP+ transceivers are listed in the below.
- Lower latency
- Lower power consumption
- Cheaper NICs and switches
- More choice of connected equipment.
- With transceivers and fiber basically any run length can be covered.
- Apparently, it is not a big deal for transmission within short distance.
- For longer runs or runs that need to go through patch panels needs transceivers and optical fiber. Fiber itself is cheap but transceivers, termination, patch panels, and etc for fiber would cost a lot.
10GBASE-T vs SFP+
This passage would mainly demonstrate the difference between 10GbE base T and SFP+ options from the respective of technology, latency, and power consumption.
Generally, 10GBase-T is cheaper and easier to deploy than the alternative SFP+ technologies. You can further compare these two different technologies in the following table:
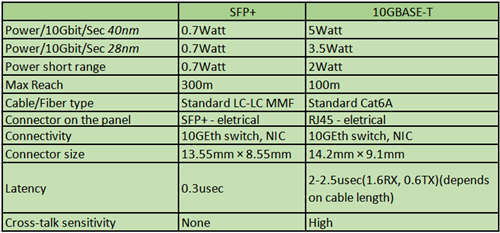
Low latency is paramount to ensure fast response time and reduce CPU idle cycles. That increases data center efficiency and ROI. With the increasing of using private cloud applications, the need for low latency is growing fast in large scale data centers.
When it comes to 10GBase-T, the PHY standard uses block encoding to transport data across the cable without errors. The standard specifies 2.6 microseconds for the transmit-receive pair, and the size of the block requires that latency to be less that 2 microseconds. SFP+ uses simplified electronics without encoding, and typical latency is around 300 nanoseconds (ns) per link. You can further compare them in the below table.
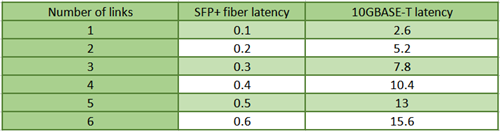
Basically, there are only slight differences between 10GBASE-T and SFP+ in terms of application latency. Relatively speaking, 10G SFP+ has lower latency than 10GBASE-T. High latency would exert negative influence on CPU and therefore limiting data center efficiency and increasing operational costs.
10GBase-T components today require anywhere from 2 to 5 watts per port at each end of the cable (depending on the distance of the cable) while SFP+ requires approximately 0.7 watt (regardless of distance). The difference is clearly shown in the below chart.
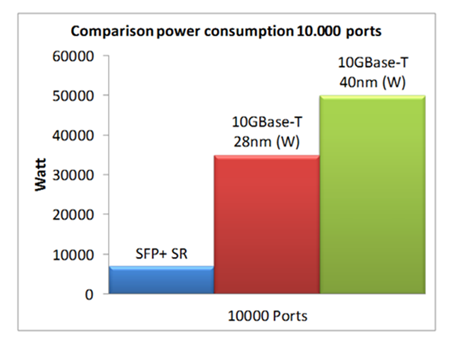
(Resource: http://www.datacenterknowledge.com)
10GBASE-T vs SFP+, Which Will You Choose
Through this article, we are clear about the pros and cons of 10GBASE-T and SFP+ as well as their differences in technology, application latency and power consumption. It is evident that SFP+ is the right technology to ensure optimal performance with lowest latency and lower power usage in the data center. The cost saving becomes obvious when deploying from 1000 to 10,000 cables in the data center.
Related Articles:
XFP vs SFP+, What’s the Difference? Can We Connect XFP and SFP+?
