As network switch evolves, there emerge various switches from different vendors, working in conditions, equipped with different functions. However, the network switches remain essentially the same despite all apparent changes. So, the following part presents the switches definition and the frequently asked question: what does a network switch do.
Purpose and Functions of a Network Switch
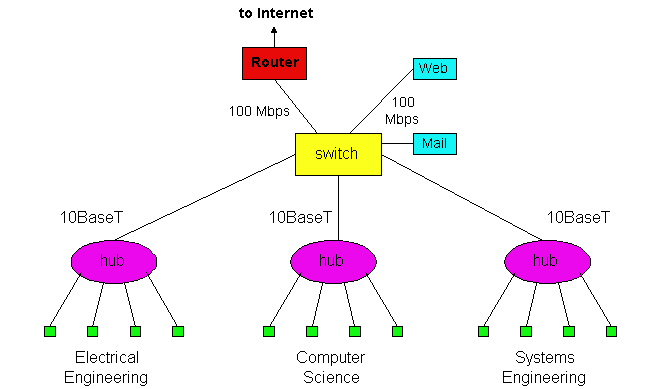
A network switch is a small hardware device that centralizes communications among various linked devices in one local area network (LAN). The fundamental function of a network switch is to exchange data packages among network devices, that is to say, the network switch gets data from any source associated with it and dispatches that data to the appropriate destination. Here take the comparison among router, hub and switch to explain what a network switch can do for our networks.
Providing More Ethernet Ports
As for network switch vs. router, network switch differs from router in the port number. Home routers usually come with three or four Ethernet ports built-in, and there are few free ports after connecting the router with the modem. So the Ethernet switch can work as the extension of router ports. In this way, it is possible to use wires to improve your speed or cut down on wireless interference.
Enabling More Intelligent Data Transmission
Network switch sends data packets to the specific one or more devices, while a hub gets the information and forwards that to every other device apart from the one that really needs the information. To develop a step further, the network switch uses full duplex mode, and communication between different pairs may get overlapped but not interrupted. Whereas in hubs, all devices have to share the same bandwidth by running in half duplex mode, causing a collision, which results in unnecessary packet retransmissions.
As for network switch vs. hub, a network switch joins multiple computers together within one local area network (LAN). A hub connects multiple Ethernet devices together, making them act as a single segment.
Three Main Types of Network Switch
To make full use of your network switch, the priority is to make clear of its function as different switches come with different capabilities. There are three types of switches in networking: managed switch, unmanaged switch, and smart or hybrid switch.
Managed Switch
Managed switch offers full management capabilities and high-levels of network security and precise control, and usually used in enterprise networks and data centers. The scalability of these switches entitles networks room to grow.
Managed switches can optimize a network’s speed and resource utilization. Admins manage resources through a text-based command-line interface, so some advanced knowledge is required to set up and run. Most managed switches are 10gb Ethernet switch, 40gb Ethernet switch and 100gb switch.
Unmanaged Switch
For unmanaged switch, the gigabit Ethernet switch itself has no settings or special features, and it exists only to add more Ethernet ports to your home network or small business offices or shops. Additionally, it is easy plug-and-play and relatively simple, so it’s great for companies without IT admins and senior technologists.
Smart or Hybrid Switch
Smart switch is partly a managed switch, as it offers functions like Quality of Service (QoS) and VLANs, but with limited capabilities that can be accessed from the Internet. Its interface is simpler than what managed switch offers. Therefore, no highly-trained staff is needed to set up or run it. It is great for VoIP phones, small VLANs, and workgroups for places like labs. In a word, smart switches let you configure ports and set up virtual networks but don’t have the sophistication to allow monitoring, troubleshooting, or remote-accessing to manage network issues.
Conclusion
The above content summarizes the issue: what does a network switch do. Based on that, three types of switches come with distinct functionality. FS offers a great range of network switches with different features. It has taken all your needs into consideration when producing and testing these switches.