A fiber optic cable, also known as optical fiber cable, is a network cable that contains two or more glass or plastic fiber cores located within a protective coating and covered with a plastic PVC outer sleeve. It’s correlated with transmission of information as light pulses along a glass or plastic strand or fiber. It’s designed for long distance, very high performance data networking and telecommunications. It has many advantages in optical fiber communication, such as large capacity, long relay distance, good security, free from electromagnetic interference and copper saving.
According to the transmission mode of light in optical fiber, fiber optic cable can be divided into single-mode fiber (SMF) and multimode fiber (MMF). Although they all belong to optical cables and aim at transmitting information, they still have some slight differences.
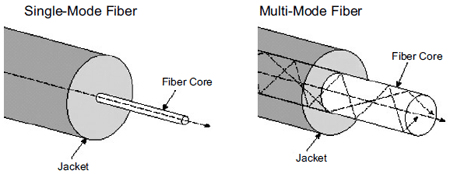
Literally, Single-mode fiber is a single stand of glass fiber with a diameter of 8.3 to 10 microns that has one mode of transmission. Due to its smaller diameter, single-mode fiber is used for long-distance signal transmission, which minimizes the reduction in signal strength. Single-mode fiber also has a considerably higher bandwidth than multimode fiber. The light source used for single-mode fiber is typically a laser, which makes it more expensive than multimode fiber.
By comparison, multimode fiber cable, with a diameter of about 62.5 microns, allows multiple mode of light to propagate through it simultaneously, thus forming mode dispersion. Mode dispersion technology limits the bandwidth and distance of multimode fiber. Therefore, multimode fiber features larger core diameter and short transmission distance. Multimode fiber typically uses an LED to create the light pulse, which makes it cheaper than single-mode fiber.
Both single-mode and multimode fiber can handle 10G speeds. The most evident difference between them lies in the distance. Within a data center, it’s typical to use multimode fiber which can get you 300-400 meters. If you have very long runs or are connecting over longer distance, single-mode fiber can get you 10 km, 40 km, 80 km, or even farther. You just need to use the appropriate optic for the distance required.
It’s widely acknowledged that optical cables are usually applied into computer networking and telecommunication due to its ability to transmit data and information. What’s more, it’s also used by military and space industries as means of communication and signal transfer, in addition to its ability to provide temperature sensing. In recent years, fiber cable is frequently used in a variety of medical instruments to provide precise illumination. An endoscope, for example, is a flexible tube containing several optical cables. When it slips into the patient’s mouth, nose, digestive tract, and other heart areas that are not visible outside the body, the doctor can see the changes through the endoscope. Other medical applications for fiber optics include X-ray imaging, biomedical sensors, light therapy and surgical microscopy.
From the aforementioned article, we can see that fiber optic cables have different types with different features, and are widely used in telecommunication, military, medical applications, etc. If you would like to know more or would like assistance in choosing the appropriate optical fiber cable, welcome to visit our website www.fs.com for more detailed information. FS will provide more choices and better services for our clients.
