Needless to say, keeping the cleanness of fiber optic connectors is essential to the high performance of optical devices. If the ferrule is damaged or broken, the whole connector will be useless. Therefore, protecting the connector ferrule from any possible contamination is very necessary. You need to take fiber optic cleaning seriously as a routine work to avoid extra loss.
From the following picture, it is clear to see that the end face of a fiber consists three areas: ferrule, cladding and core. Once these parts are free from contamination, fiber optic cleaning is complete. Different contaminants may result in different cleaning solutions. Do you know how many kinds of contaminants are there on the fiber optic connectors?
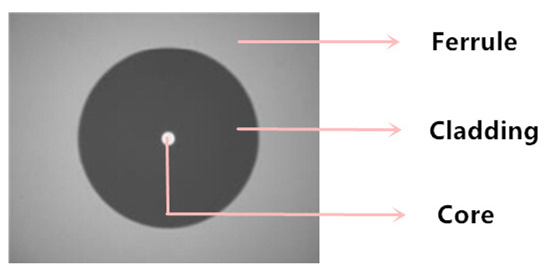
Generally speaking, there are three types of contaminants. Dusts and oils are the most common types. Cleaning these contaminants is easier as long as using the proper method. However, the contaminant of scratches, chips or pits sometimes may cause permanent defects on the end face. Then a new connector is required for replacement. Oils from your fingers will leave a noticeable defect easily seen with the use of a fiber scope, but it will also tend to trap dust against the fiber, which can lead to scratches on both the fiber connector and the optic it is being mated to. In addition, when installing or removing a fiber, small static charge on the ends will attract dust particles in the air. Therefore, putting on the fiber caps is a good precaution if the cable is not used.

Nevertheless, if the connector is already polluted, using fiber caps will no longer be enough. Proper cleaning methods should be applied to remove the contaminants. Here lists some common cleaning methods:
- Dry cleaning – No solvent is used for this type of method. The whole cleaning is processed in a dry condition.
- Wet cleaning – Solvent is required for this method. Isopropyl alcohol is the most common solvent.
- Non-abrasive cleaning – This method will not use any abrasive material to contact the connector end face.
- Abrasive cleaning – This method will adopt abrasive tools such as lint-free wipes to do the cleaning.
If you have decided the cleaning method, then it is time to choose the right cleaning products. Common cleaning solutions on the market now are the pen cleaner, cassette cleaner, cleaning card and wipes.
Pen cleaner is also named as one-push cleaner. It features an easy one push action, which quickly and effectively cleans the end-face of connectors. The cleaning tip is rotated to ensure the fiber end-face is effectively but gently cleaned. Usually available for 600 to 800 cleans.

Cassette cleaner or reel-type cleaner is ideal for lab, assembly line and field use. It enables simple push bottom shutter operation for quick and easy cleaning. Each cleaning tape is available for 400 to 500 cleans.
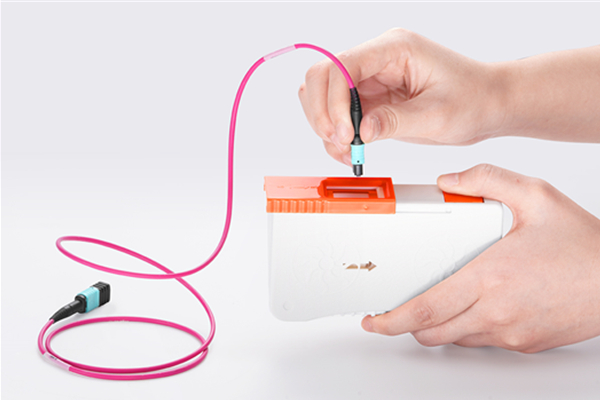
Cleaning card is made of the densely woven micro fiber cloth which effectively minimizes the static charge. Wipes are designed with minimal lint or dust to have little interference with the normal functioning of the equipment.

Follow these steps, you can always make a thorough fiber optic cleaning:
- Step 1, inspect the fiber connector with a fiber scope.
- Step 2, if the connector is dirty, clean it with a dry cleaning technique.
- Step 3, inspect the connector.
- Step 4, if the connector is still dirty, repeat the dry cleaning technique.
- Step 5, inspect the connector.
- Step 6, if the connector is still dirty, clean it with a wet cleaning technique followed immediately with a dry clean in order to ensure no residue is left on the end face.
- Step 7, inspect the connector again.
- Step 8, if the contaminant still cannot be removed, repeat the cleaning procedure until the end face is clean.
Constantly cleaning the fiber optic connectors can greatly decrease the link failures and unnecessary component replacement. Moreover, using professional tools is much safer and cleaner. Are you ready to clean the fiber optic connectors from now on?


